Breast Augmentation
Enhance your natural curves
Breast augmentation is a deeply personal decision, and at Allura Clinics, we are here to guide you every step of the way. Whether you want to enhance volume, restore balance, or achieve a more proportional shape, our expert team ensures your journey is safe, comfortable, and tailored to your needs.
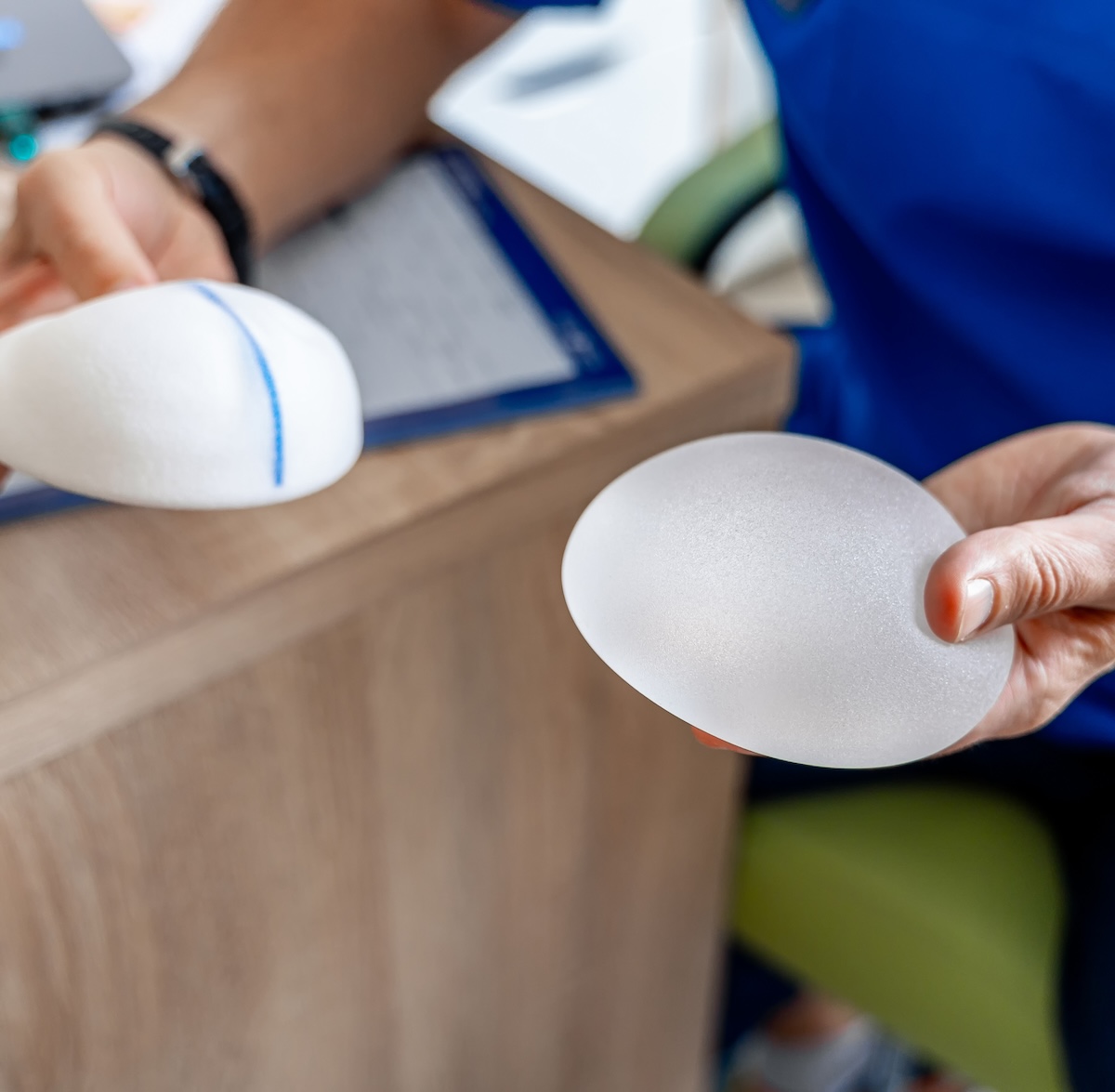
Choosing the right implant is key to achieving the look and feel you want. At Allura Clinics, we offer three main types of implants:
During your consultation, Dr. Husain will help you determine which implant best suits your body and aesthetic goals.
Every patient has unique preferences and body proportions, and selecting the right size is a crucial step in the process. This decision will be discussed in detail during your consultation, where we will consider your anatomy, lifestyle, and personal goals. Using advanced imaging techniques, we ensure your chosen size complements your overall figure.


Yes, breast augmentation is an effective way to improve breast symmetry. Many women have naturally uneven breasts, and implants can help balance size, shape, and volume for a more harmonious look. If asymmetry is a concern, Dr. Husain will create a customized approach to ensure a beautifully even result.
Most women can breastfeed after breast augmentation. Studies show that even if you never have breast surgery in your life, the chance you can breastfeed is about 75%. If you do have breast surgery, for example breast augmentation, the chance you can breastfeed is also 75%. So there is no guarantee you can breastfeed after surgery, but there is no guarantee anyway.
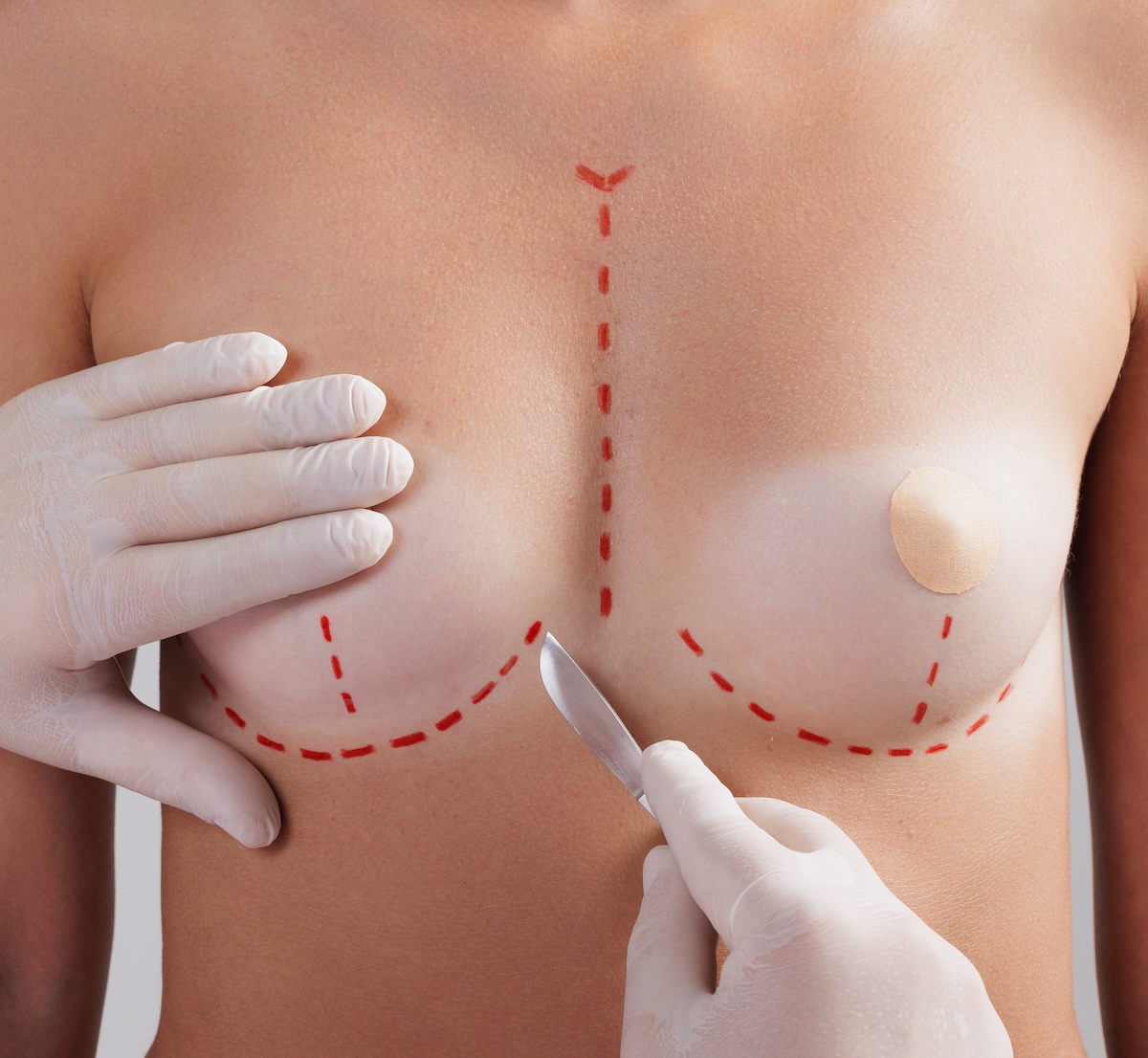

One of the most common concerns is whether breast implants will feel natural. The answer depends on several factors, including implant type, placement, and the amount of natural breast tissue you have. Silicone tend to provide the most realistic feel. Additionally, placing the implants under the muscle can enhance the natural look and movement.
At Allura Clinics, we prioritize natural-looking results that move and feel as close to natural breast tissue as possible.
Breast augmentation is one of the most commonly performed cosmetic procedures and has a well-established safety record. Like any surgery, it carries some risks, including infection, capsular contracture, and implant rupture. However, these risks are minimized when performed by a skilled surgeon.
At Allura Clinics, we prioritize patient safety by using the latest techniques, high-quality implants, and advanced surgical methods to achieve optimal results with minimal risk.
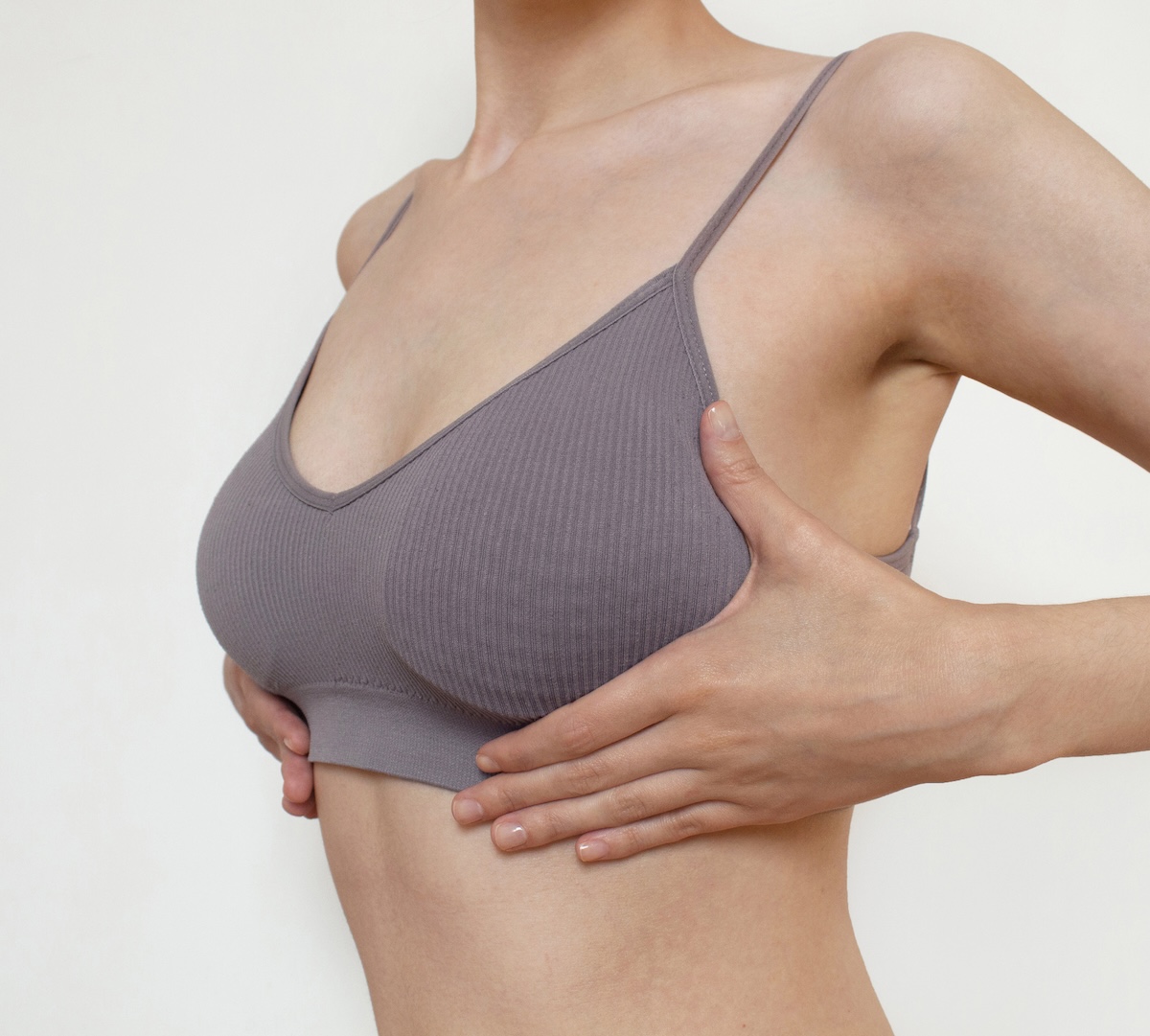

Breast augmentation is a straightforward procedure performed under general anesthesia. The surgery typically lasts two hours and involves making a small incision below the breast, creating a pocket for the implant under the muscle, inserting the implant, and positioning it for optimal shape and symmetry. Common incision locations include:
Dr. Husain will recommend the best incision and placement technique based on your anatomy and goals.
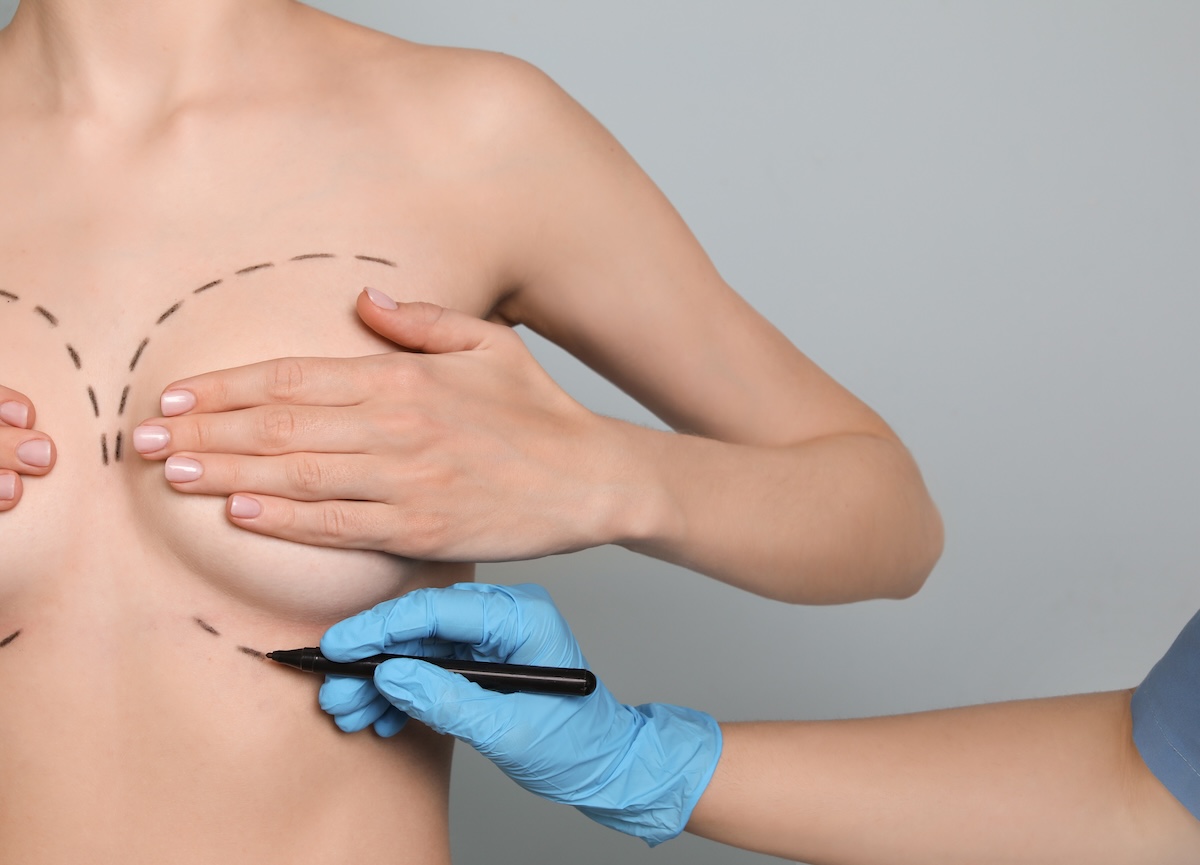

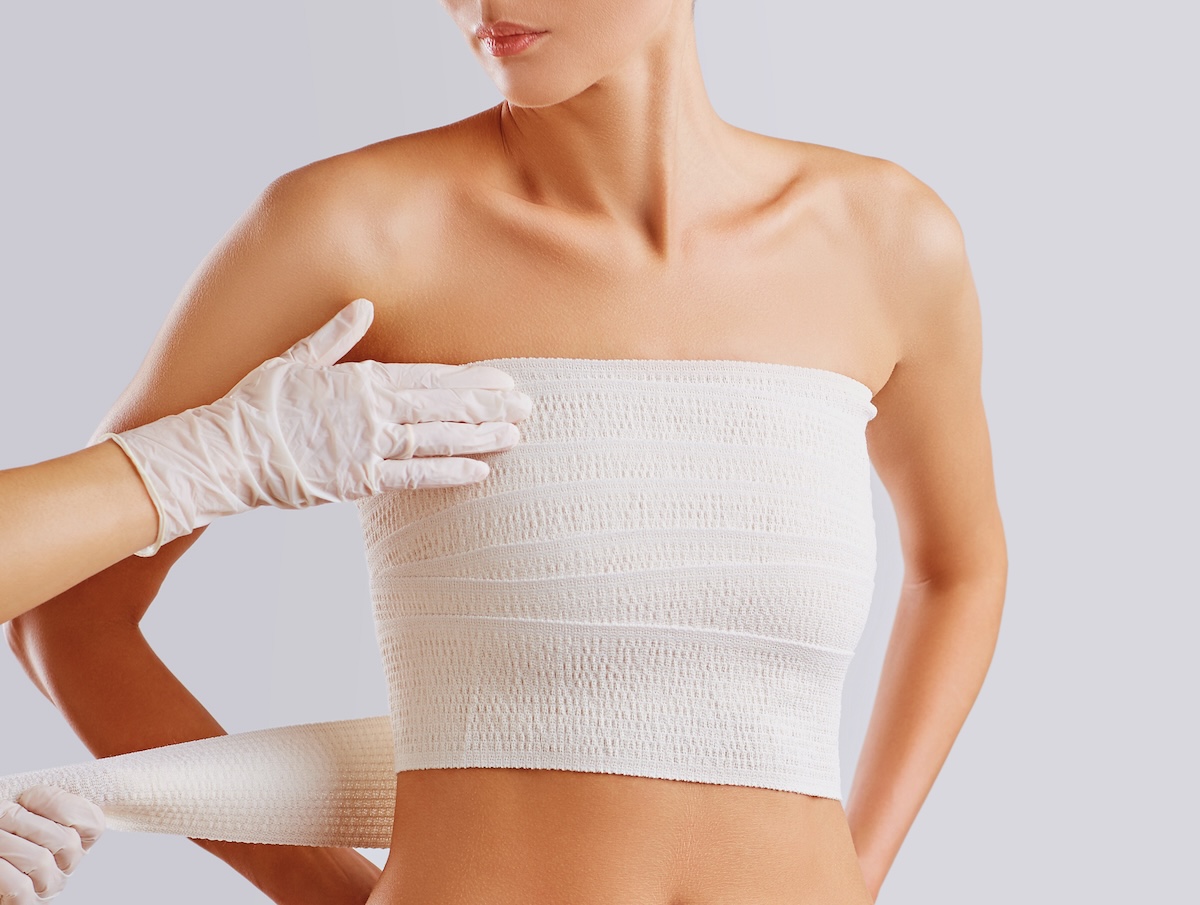
After surgery, you can expect some swelling, tightness, and mild discomfort, which will gradually subside. Most patients return to light activities within a few days and resume normal routines within a few weeks. Key recovery milestones include:
Our team will provide personalized aftercare instructions to ensure a smooth recovery.


Dr. Husain is a highly respected cosmetic surgeon known for his expertise in breast augmentation and body contouring. With years of experience and a commitment to excellence, he takes a personalized approach to every procedure. His goal is to create results that enhance your natural beauty while maintaining harmony with your body.
At Allura Clinics, Dr. Husain and his team focus on patient education, comfort, and safety to ensure you feel confident throughout your journey.
ABOUT DR HUSAIN

Choosing to undergo breast augmentation is an exciting step toward achieving the look you desire. At Allura Clinics, we understand the importance of feeling informed, supported, and comfortable with your decision.
We invite you to schedule a consultation with Dr. Husain to discuss your goals, ask any questions, and receive expert guidance on the best approach for you.
Take the next step toward feeling confident in your body. Book your consultation today and let us help you achieve the beautiful, natural results you deserve.
BOOK A CONSULTATION